ISSN 2232-9080
No. 15, June 2018.
Dear readers,
Before you is one more issue of the e-Zbornik this time along with an English version as well.
Just like the one before, you can find this issue in the EBSCO Academic Search, in the database of the Engineering Source following this link: https://www.ebscohost.com/academic/engineering-source.
Since the last issue you can also find us in the portal of scientific journals of the Republic of Croatia, HRČAK at the following link: https://hrcak.srce.hr/.
We would like to thank everyone who contributed in the creation of this issue.
We are looking forward to future collaboration.
Ivana Domljan, editor of the 15th issue HRVATSKI
THE IMPORTANCE OF VISION-BASED TECHNOLOGIES FOR PROGRESS MONITORING AND PRODUCTIVITY ASSESSMENT OF EARTHMOVING OPERATIONS
Martina Šopić, M. Eng. C. E.
University of Rijeka, Faculty of Civil Engineering
Mladen Vukomanović, Ph. D.
University of Zagreb, Faculty of Civil Engineering
Diana Car-Pušić, Ph. D.
University of Rijeka, Faculty of Civil Engineering
Abstract: Monitoring the progress of earthmoving operations while accurately estimating productivity of construction equipment provides a detailed insight into the performance, early detection of low productivity, as well as any other possible defects. It also provides feedback on the correctness of the decisions made and a more accurate report of the time and cost necessary for the activity. Early detection and warning of all the risky, unfavorable actions provides opportunities to timely take appropriate corrective measures and make improvements. Wireless technologies offer considerable potential for application in order to monitor work progress and evaluate productivity. However, the previous studies indicate shortcomings and limitations. Future research attention on their considerable potential is needed. The integration of various wireless technologies is a possible solution to the problem and complexity of monitoring work progress and productivity estimates. In this matter, vision-based technologies are an indispensable field of wireless technologies for the development of an appropriate, reliable, credible, fast and cost-effective methodology of monitoring the progress of earthmoving works with accurate estimation of the productivity of construction machines.
Key words: vision-based technologies, progress, productivity, earthmoving
CHANGES IN THE CONSTRUCTION PROCESS AND THE ROLES IN BIM IMPLEMENTATION ON THE EXAMPLE OF A PUBLIC UTILITY BUILDING
Ivan Janjić, M. Eng. C. E.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek (student)
Dina Stober, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek
Zlata Dolaček-Alduk, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek
Abstract: Resource savings requirements in projects that result from the global resource-saving need stimulate innovation in construction, both in the field of innovative materials and products, and in the improvement of all construction processes. Changes in the project are marked by risks and usually assume the need for additional resources - time and money. Change management differs for a project that is traditionally conducted in a consecutive way from project design to project submission and to a project developed by the BIM approach that seeks to put processes more and more simultaneously. This paper presents a review of the literature that defines the differences between these two approaches and establishes a framework for exploring the possibilities for improving the complex building project created and managed by traditional approach based on the theoretical background.
Key words: changes in project, BIM approach, public utility building, Faculty of Civil Engineering Osijek
DETERMINATION OF THE SOIL REACTION COEFFICIENT VALUE – SOFTWARE SOLUTION
Vlaho Akmadžić, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Mostar
Anton Vrdoljak, M. Sc.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Mostar
Abstract: In numerical modeling of structures, it is necessary to model the soil on which the structures rest. This soil simulation is performed through the Winkler springs model. In the simplest case of shallow foundations, this is done through the coefficient of soil reaction. Since a large number of authors have dealt with this topic, for the needs of a more reliable modeling, the SE_Calc software solution has been developed. The subgrade reaction is calculated on the templates of several authors in order to graphically display their relationships.
Key words: numerical modeling, subgrade reaction, software solution
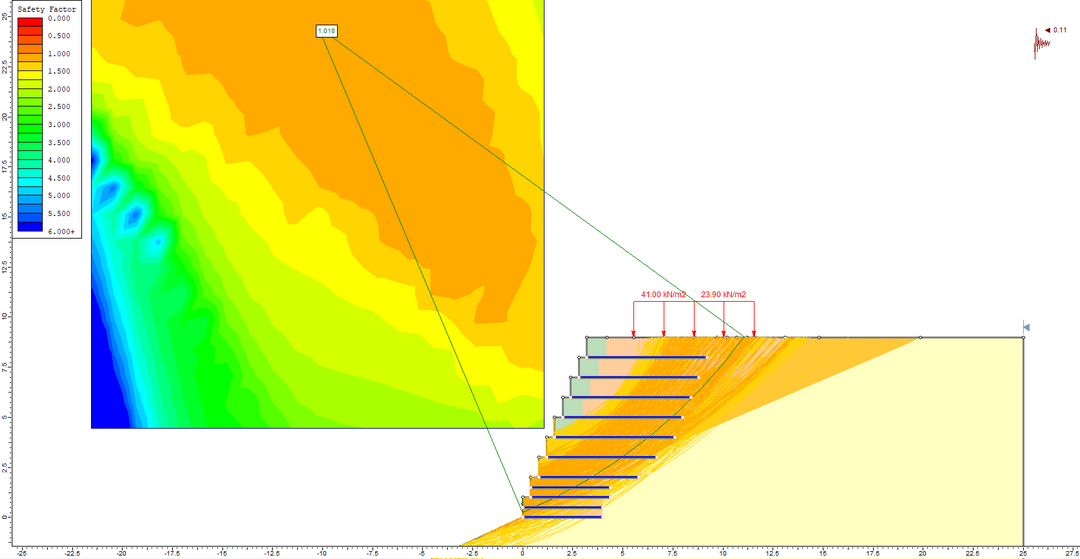
DESIGN OF REINFORCED GABION WALL: EXAMPLE OF RETAINING WALL FOR "VIDIKOVAC" REST AREA ON THE ISLAND OF BRAC
Predrag Miščević, Ph. D.
University of Split, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture and Geodesy
Goran Vlastelica, Ph. D.
University of Split, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture and Geodesy
Marino Babić, M. Eng. C. E.
University of Split, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture and Geodesy
Abstract: For purpose of constructing the "Vidikovac" rest area on the state road D115 Humac - Bol, not far from town of Bol on the island of Brač, a 9m retaining wall was necessary to form a plateau. Since the denivelation could not be formed as cascading, due to the request space for rest area, options for the construction of a 160 m long classically reinforced concrete wall and a gabion wall were investigated. The gabion wall with reinforced backfill was selected. Calculation sequence, as well as advantages and disadvantages of this type of construction are presented in this paper.
Key words: gabion, reinforced backfill, retaining wall, design, rest area
ANALYSIS OF LEVELING NETWORK OF VIADUCT KOŠEVO
Admir Mulahusić, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Sarajevo
Jusuf Topoljak, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Sarajevo
Nedim Tuno, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Sarajevo
Naida Ademović, Ph. D.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Sarajevo
Ernes Vojniković, M. Sc.
Municipality of Sanski Most
Abstract: Special vertical geodetic network was established on the viaduct Koševo. Measurements in the network were performed by using precise geometric leveling in two epochs. Measurements in the first epoch were done in winter conditions, while the second epoch measurements were done in summer conditions. Processing and network adjustment was followed after the measurements. The heights of characteristic points on the bridge resulted from mentioned procedure. Taking into account the standard deviation of measurements, differences in heights of points on the bridge have shown change in the height of individual points on the bridge. These differences suggest possible movements of the pre-stressed concrete viaduct Koševo.
Key words: bridge, precise leveling, adjustment, results analysis
ANALYSIS OF BUS STATION PAVEMENT STRUCTURE CONDITION IN THE CITY OF RIJEKA
Marijana Cuculić
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Rijeka
Aleksandra Deluka Tibljaš
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Rijeka
Ivana Pranjić
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Rijeka
Miran Flego
Geoprojekt d. d. Opatija
Abstract: Road network condition deteriorates over time because of the climatic and meteorological conditions, traffic loading and insufficient maintenance. Bus stations on urban road network are especially exposed to premature damage appearance due to specific loading conditions. In this paper an analysis done at the chosen bus stations in Rijeka city is presented. Different parameters were measured and analysed and suggestions for maintenance of analysed pavements are defined.
Key words: pavement structure, bus stations, distress
USE OF ALTERNATIVE TYPES OF ROUNDABOUTS IN MOSTAR CITY FOR URBAN SUSTAINABILITY
Danijela Maslać, B. S. C. E.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Mostar
Abstract: The aim of the paper is to justify the construction of alternative roundabouts in the city of Mostar for the purpose of urban sustainability and by satisfying criteria. Namely, in urban environments, due to the limited space available, it is often necessary to investigate the possibility of applying non-standard solutions that can satisfy all the necessary criteria. Alternative types of roundabouts in the reconstruction of Kralja Tvrtka Street in the Mostar city are presented.
Key words: alternative types, roundabouts, urban sustainability, performance criteria
MOSTAR AREA LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE DETERMINATION WITH SATELLITE METHODS
Tea Duplančić Leder
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Architecture, and Geodesy, University of Split, full professor
Nenad Leder
Faculty of Maritime Studies, University of Split, assistant professor
Abstract: The article briefly presents the most critical factors that affect the soil temperature. Most of these factors can be found in city of Mostar area. The simplest and the most widely used method of land surface temperature determination is processing of thermal bands of satellite scenes. Landsat is the longest and most widely used satellite mission with open data. For the purposes of this study Landsat 5, 7 and 8 satellite scenes and open meteorological data were used, from which the atmospheric correction, and then land surface temperature (LST), were calculated for Mostar area. Four winter scenes (taken in the colder part of the year) and four summer scenes (taken in the warmest part of the year) were used. From all processed data, it can be concluded that Mostar can be considered as one of the warmest cities in Bosnia and Herzegovina and wider.
Key words: Land surface temperature, Landsat mission, remote sensing, urban heat islands
PREPARATION OF WATER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR ADRIATIC RIVER BASIN DISTRICT IN FEDERATION OF B&H
Damir Mrđen, B. S. C. E.
Adriatic Sea River Basin District Agency, Mostar
Ivan Matković, B. Sc. (Forestry)
Adriatic Sea River Basin District Agency, Mostar
Mirko Šarac, B. S. C. E.
Adriatic Sea River Basin District Agency, Mostar
Abstract: According to Water Act in Federation of B&H, Water Management Strategy in Federation of B&H and EU Water Framework Directive (WFD), it is necessary to prepare and adopt Water Management Plan for Adriatic River Basin District in Federation of B&H (river basins of Neretva with Trebišnjica, Cetina and Krka in Federation of B&H). The aim is achieving of the required good ecological status and/or good ecological potential for all water bodies and prevention of further deterioration as well as protection and improvement of the status of aquatic ecosystems. Main activities during the preparation and adoption of SEA for this Plan are also presented.
Key words: EU WFD, Water Act in FB&H, Water management strategy in FB&H, water bodies, good status/potential of water bodies, SEA
KEY PRINCIPLES OF WATER TARIFF METHODOLOGY
Branko Vučijak
Mechanical Engineering Faculty of University of Sarajevo, Associate Professor
Abstract: Regulatory framework for water supply services in different Balkan countries does not provide the necessary level of self-sustainability of these services, and they are searching for the needed improvements. Management of water supply service providers usually point out the tariff rates as critical to their operations, together with the level of non-revenue water, staff number and expertise and eventually collection of receivables. Even more, high non-revenue water is often justified with existing low tariff, claiming that it cannot cover all costs and the first activity that is usually left without financial resources is regular renewal and reconstruction of the network, causing real network losses grow year after year.
Since any needed costs recovery can be assured with sufficient rise of price and adequate collection rate, water supply managers often underline that the EU legislation requests for "cost recovery" as one of the key principles of tariff setting. Even more, wording is often extended to "full cost recovery", thus stressing that it is not only operational costs to be recovered. But at the same time limited observations are made to other key principles that would keep the tariff justified and affordable.
The paper discusses several additional principles to be observed, as well as their visibility within the legal environment of the selected Western Balkan countries.
Key words: water tariff, tariff methodology, key principles, cost recovery, economic efficiency






